Enzyme cost minimization
Main | Workflow | Model | Running ECM | Download
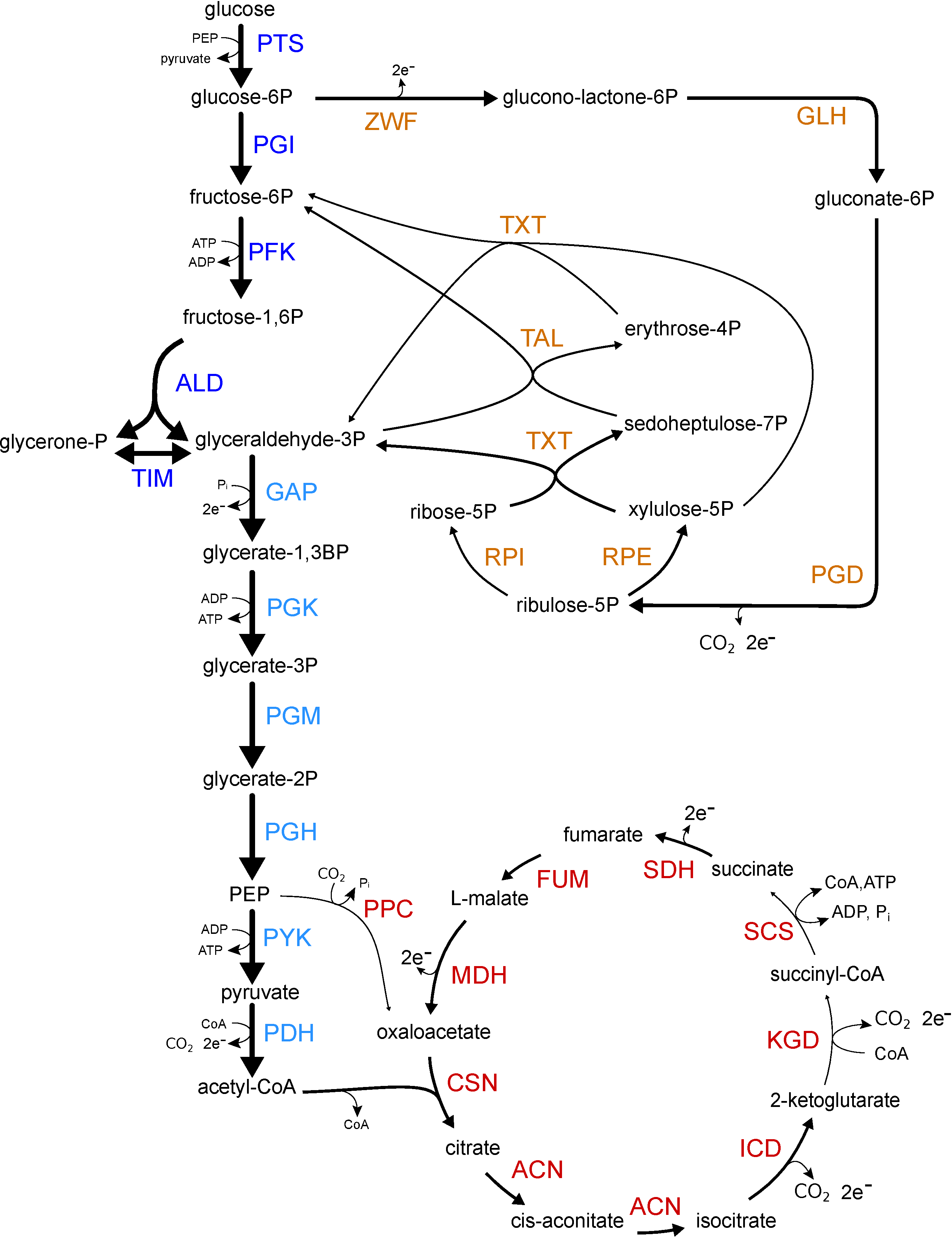 |
Escherichia coli model As
an example, we constructed a kinetic metabolic model
of E. coli central metabolism and predict its
metabolite and enzyme levels.
|
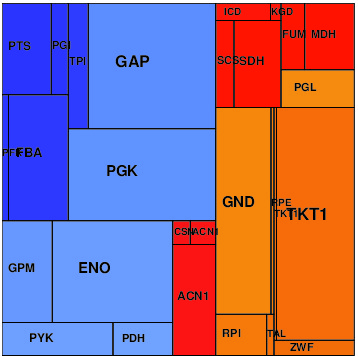
Results
Simulation results can be found below in several data formats: in the SBtab table format (for models and data) and SBML (for models only). The NEOS files can be used for running optimizations on the NEOS Optimization Server.
| Uniform protein cost | Size-dependent cost | Composition-dependent |
 |
 |
 |
| Results [.pdf] | Results [.pdf] | Results [.pdf] |
| Input data | Input data | Input data |
| Network model [SBML] | Network model [SBML] | Network model [SBML] |
| Model and data [SBtab] | Model and data [SBtab] | Model and data [SBtab] |
| Model and data [NEOS files] | Model and data [NEOS files] | Model and data [NEOS files] |
| Result files | Result files | Result files |
| Model and EMC4cm run [SBtab] | Model and EMC4cm run [SBtab] | Model and EMC4cm run [SBtab] |
| Metabolic states [SBtab] | Metabolic states [SBtab] | Metabolic states [SBtab] |