Economics of periodic enzyme activities
Main | Pathway models | More models | Article preprint
Oxidation and reduction (dynamic)
This model illustrates the idea that metabolism could oscillate, on the one hand, between between oxidative and reductive phases and, on the other, between high-energy and low-energy phases (with high or low ATP levels, respectively). In a first reaction (central metabolism(, substrate is converted into rediction equivalents (e.g., NADH produced in the TCA cyle). A second reaction (oxidative phosphorylation) converts reduction equivalents into ATP. A third reaction (anabolism) consumes NADH and ATP to produce biomass.
| Forced oscillation (without adaptation) | Spontaneous rhythm |
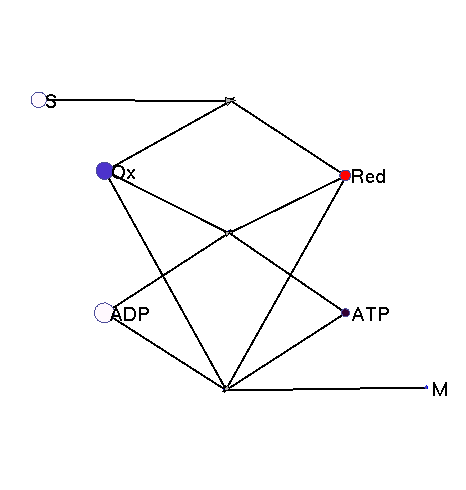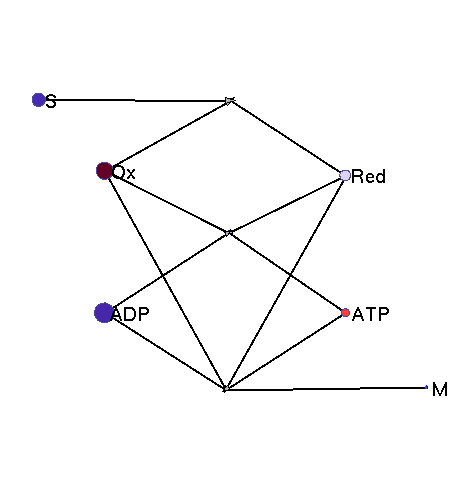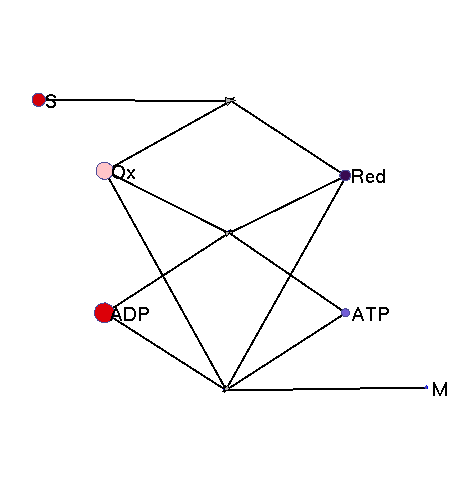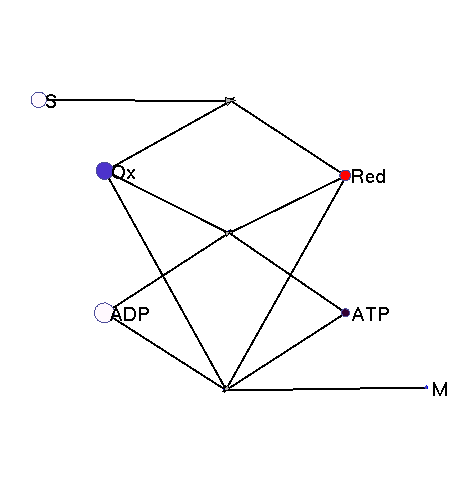 |
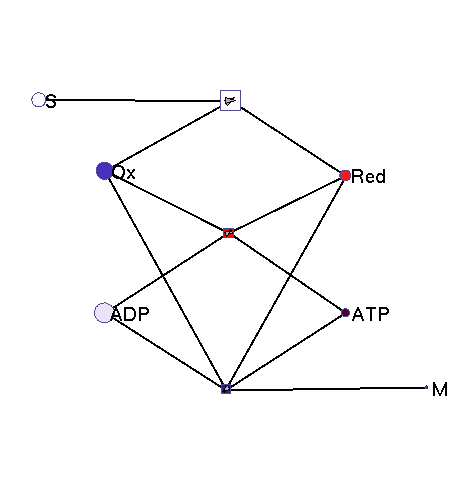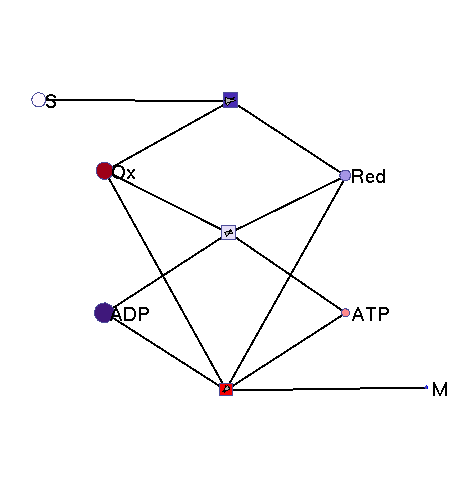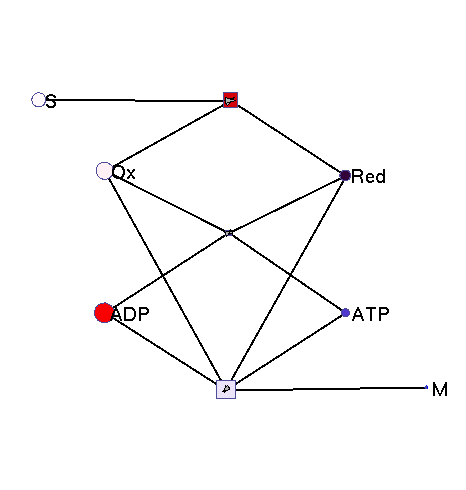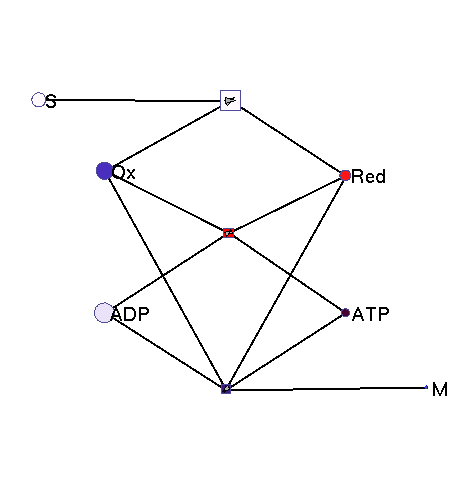 |
Squares: enzyme levels Circles: metabolite levels