Economics of periodic enzyme activities
Main | Pathway models | More models | Article preprint
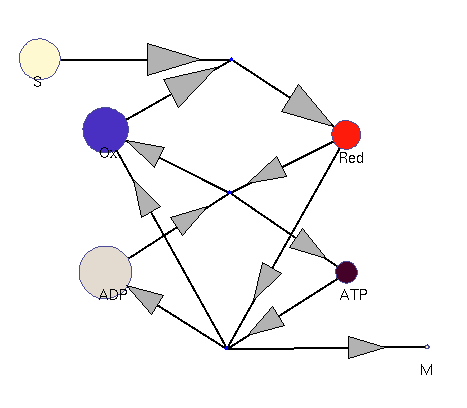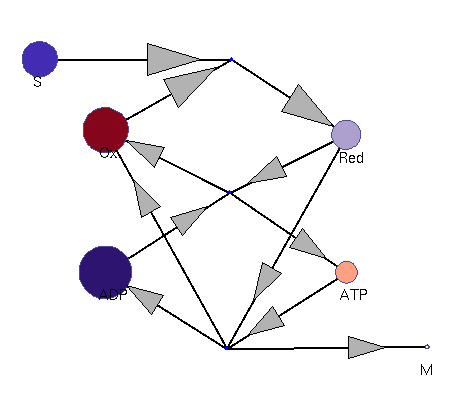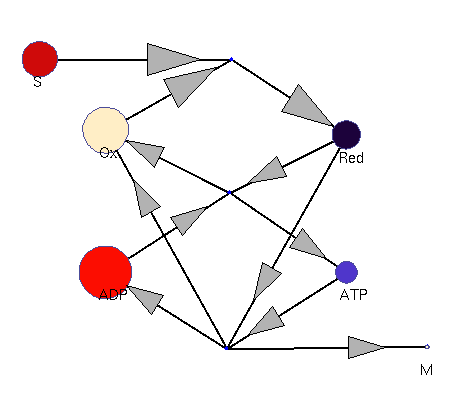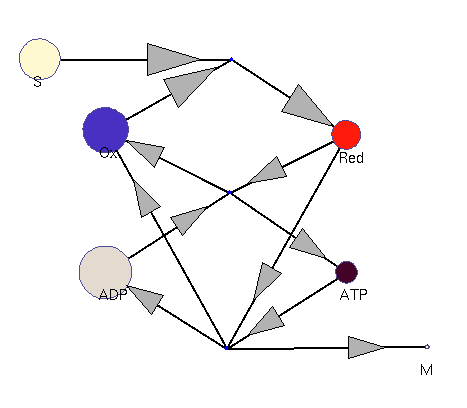
Oxidation and reduction (dynamic; fast adaptation)
This model illustrates the idea that metabolism could oscillate, on the one hand, between between oxidative and reductive phases and, on the other, between high-energy and low-energy phases (with high or low ATP levels, respectively). In a first reaction (central metabolism(, substrate is converted into rediction equivalents (e.g., NADH produced in the TCA cyle). A second reaction (oxidative phosphorylation) converts reduction equivalents into ATP. A third reaction (anabolism) consumes NADH and ATP to produce biomass.
| Forced oscillation (without adaptation) | Spontaneous rhythm |
 |
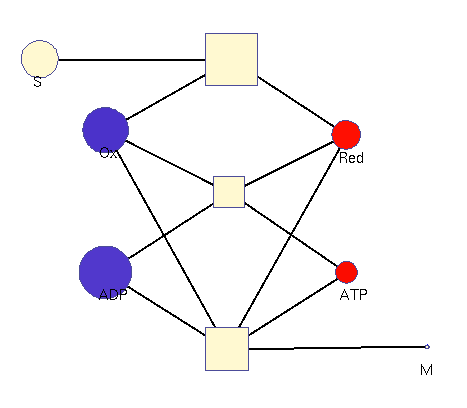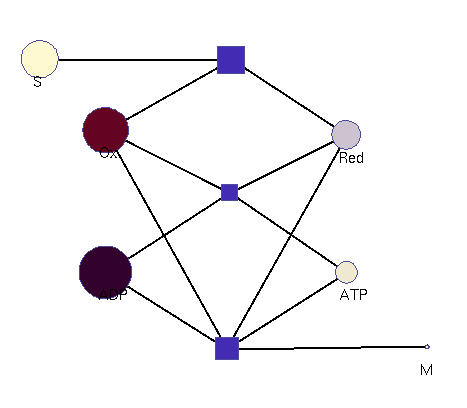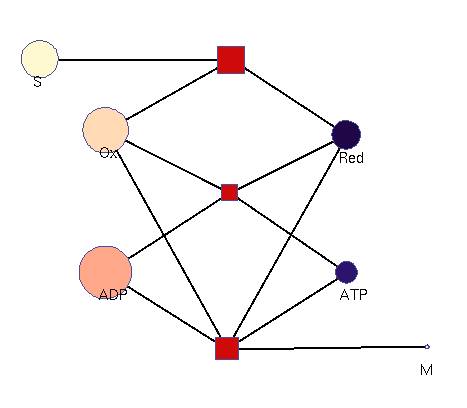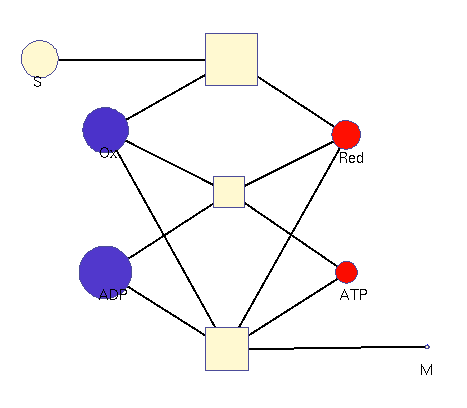 |
Squares: enzyme levels Circles: metabolite levels