Economics of periodic enzyme activities
Main | Pathway models | More models | Article preprint
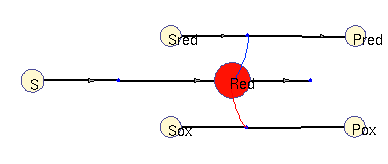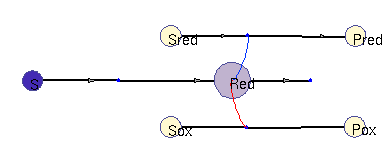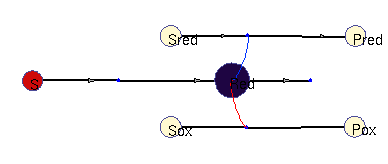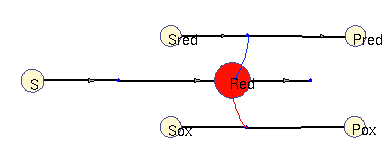
Oxidation / reduction model (allosteric)
In this model, a (periodic) substrate is converted into an intermediate (which represents reduction equivalents), which is then non-enzymatically degraded. There are two other enzymatic reactions: one requires reduction equivalents, (top), the other one works better without them (bottom). For simplicity, the effects reduction equivalents are modelled as allosteric regulations. The benefit function scores the sum of all three enzymatic reactions. In the optimal solution, the first enzyme is periodically adapted to its substrate and promotes phase-shifted rhythms in the other enzymes (approximately synchronous, and approximately anti-phasic).
| Forced oscillation (without adaptation) | Forced oscillation (with adaptation) |
 |
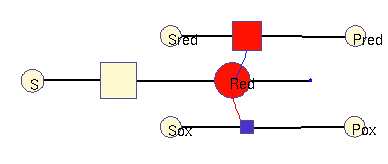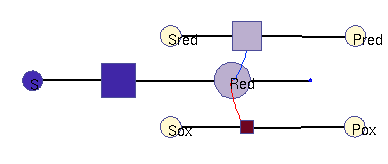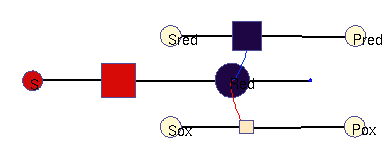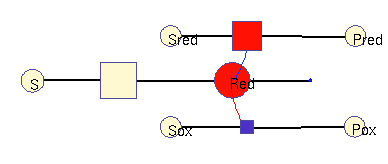 |
Squares: enzyme levels Circles: metabolite levels